CBC – Cannabichromene
What is CBC Cannabichromene used for?
Cannabichromene, or CBC, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. CBC has recently become one of the most studied cannabinoids for its potential medicinal benefits. It is known to have anti-inflammatory properties and has been suggested as a possible treatment for chronic pain, acne, anxiety and depression, as well as being protective against tumor growth. As research continues to explore its possible therapeutic applications, CBC could prove to be an exciting new therapy option for many medical conditions.
Cannabichromene (CBC) is an important cannabinoid found in Cannabis sativa and hemp plants that binds to receptors in the brain, heart, lungs, and other bodily organs. It has been found to have a variety of beneficial effects including being anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, analgesic, anti-tumorigenic, anti-epileptic and neuroprotective. Studies suggest CBC may help with muscle relaxation and when used in combination with other cannabinoids can produce a more powerful entourage type effect on the body. CBC also may improve mood and encourage positive feelings among users similar to its counterpart THC. It is non-intoxicating making it an attractive option for people wanting relief from conditions such as depression or chronic pain without the “high”. From a therapeutic perspective then, CBC is excellent offering multiple physiological benefits whilst avoiding any psychoactive effects which individuals may not want or need.
Shop Potluck Expo CBC products >>
What is the history of Hemp Cannabis CBC Cannabichromene?
CBC was discovered and isolated for the first time in 1966 by an extraction process on hashish with hexane, later also through a percolation with benzene directly from cannabis plants. Because of its peculiar qualities and benefits, from 2015 various medicinal preparations containing high quantities of Cannabichromene were released on the market.
How is CBC extracted or made in a lab?
CBC is made through selective breeding of plants to create strains with higher concentrations of this particular cannabinoid. Additionally, it can be synthesized in a laboratory by reacting cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) with heat and an alkali such as calcium hydroxide, which yields CBC resins that are further purified and crystallized into the final product.
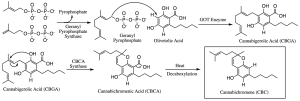
When synthesizing CBC from CBDA. First the plant produces a precursor called CBGA, cannabigerolic acid. This precursor, based on the action of the enzymes present in the different strains of Cannabis, forms 3 main cannabinoids in different concentration:
- THCA (tetrahydrocannabinol acid);
- CBDA (cannabidiolic acid);
- CBCA (Cannabicromenic acid).
Through a process of decarboxylation by exposure to heat or ultraviolet rays , CBCA finally becomes CBC. The process is very similar to the one that brings to the formation of THC and CBD.